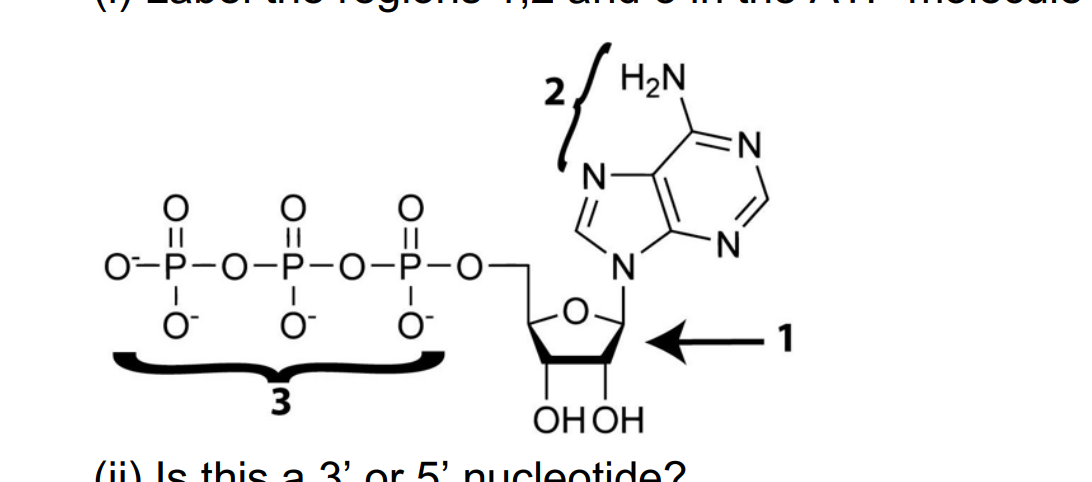
41 atp molecule with labels
Magnesium in biology - Wikipedia Magnesium is an essential element in biological systems.Magnesium occurs typically as the Mg 2+ ion. It is an essential mineral nutrient (i.e., element) for life and is present in every cell type in every organism. For example, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the main source of energy in cells, must bind to a magnesium ion in order to be biologically active. Draw the structure of ATP molecule. Label the high energy bonds ... Draw the structure of ATP molecule. Label the high energy bonds.\( P \)W📲PW App Link - 🌐PW Website -
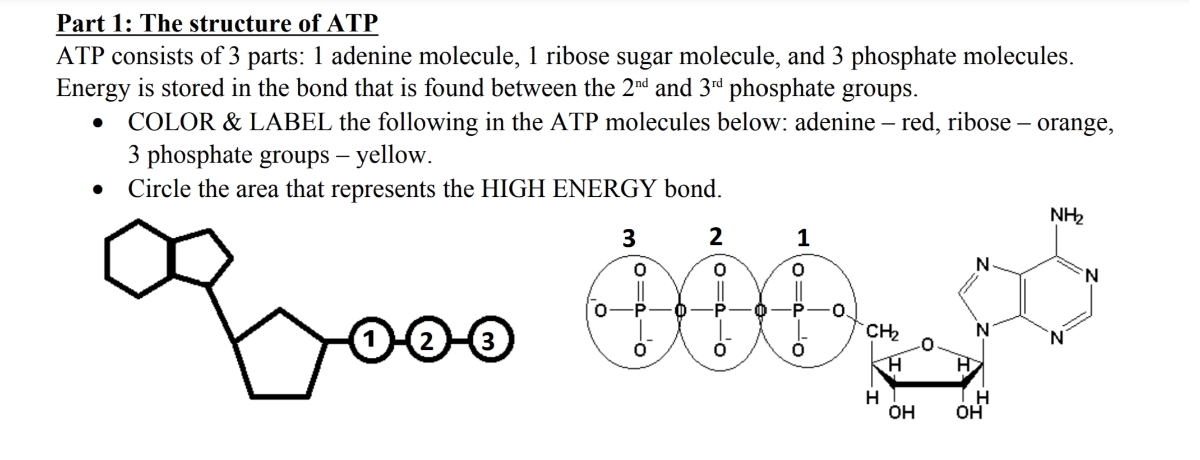
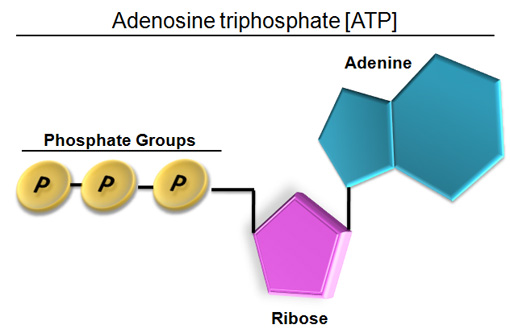
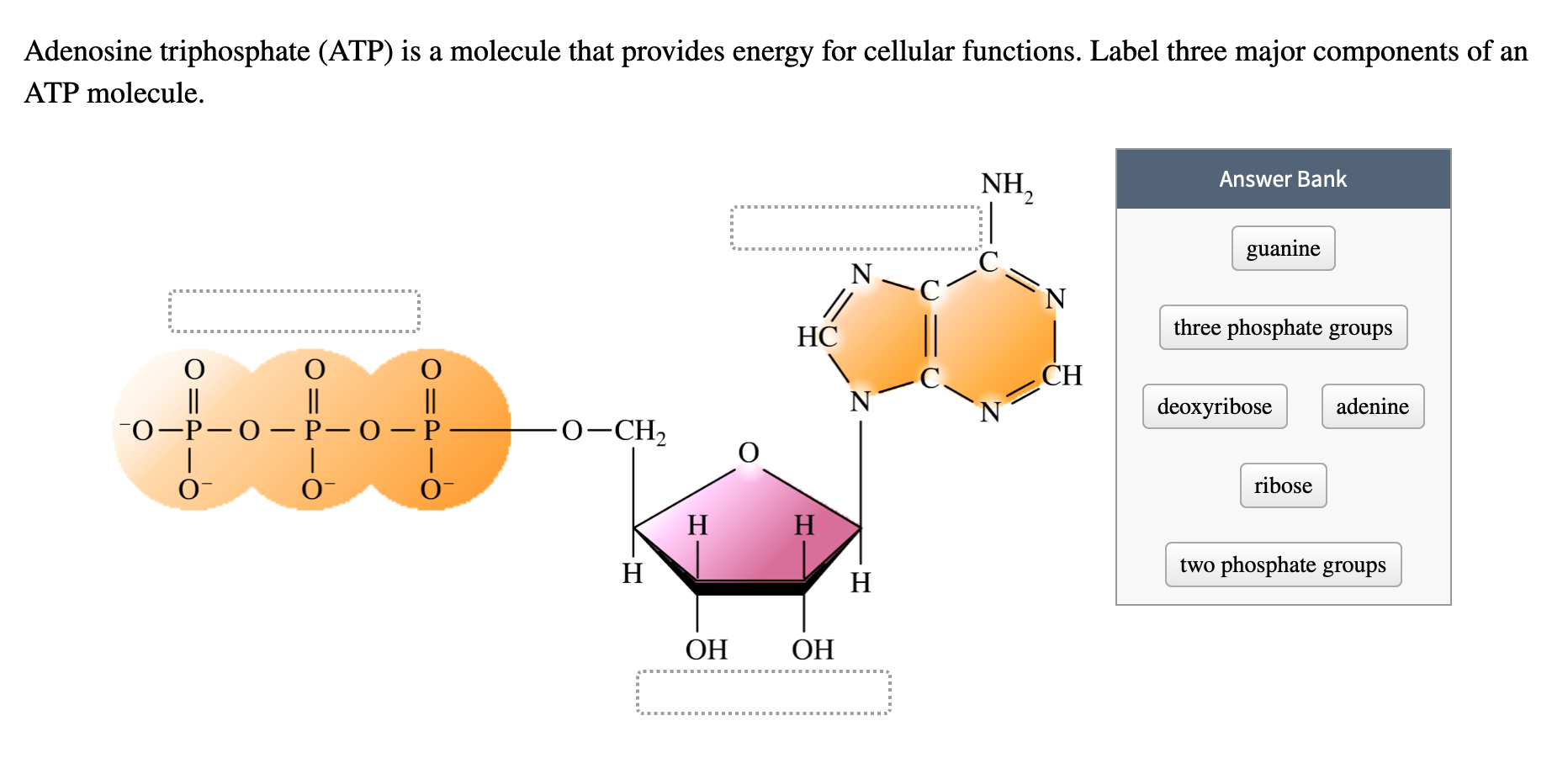
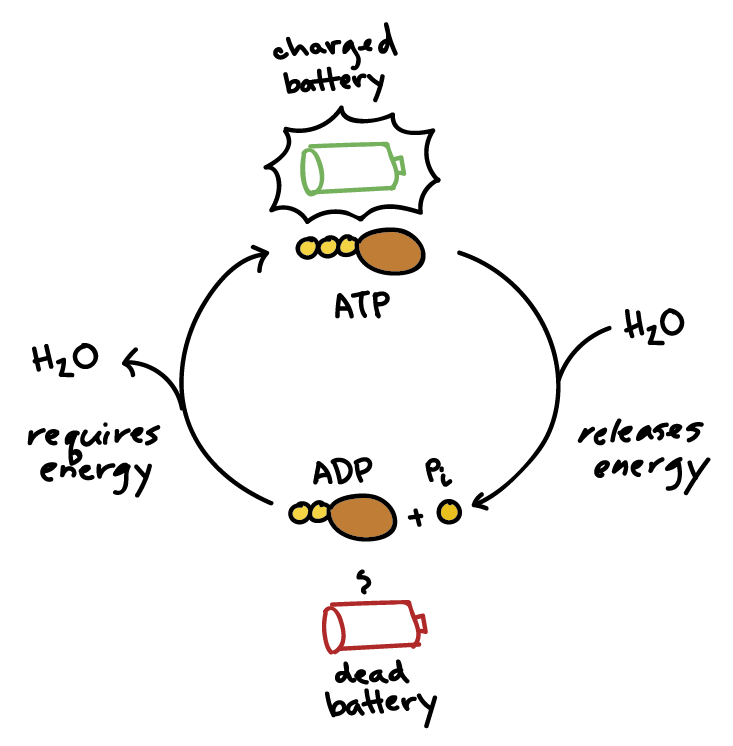
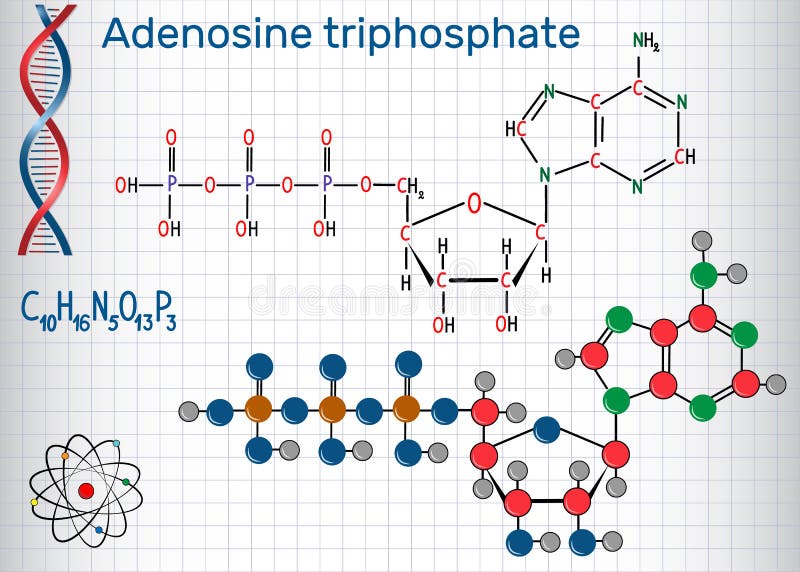
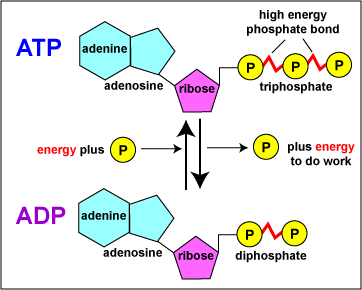
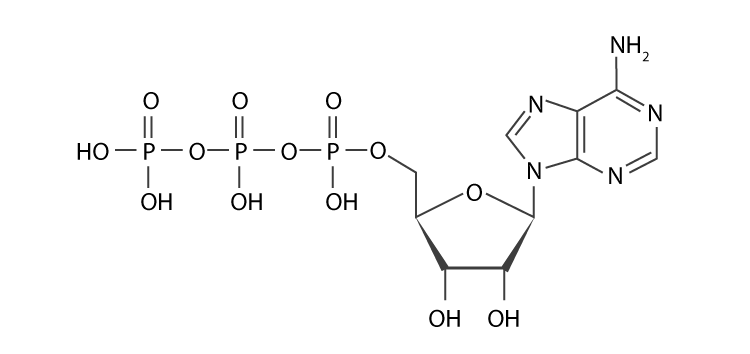
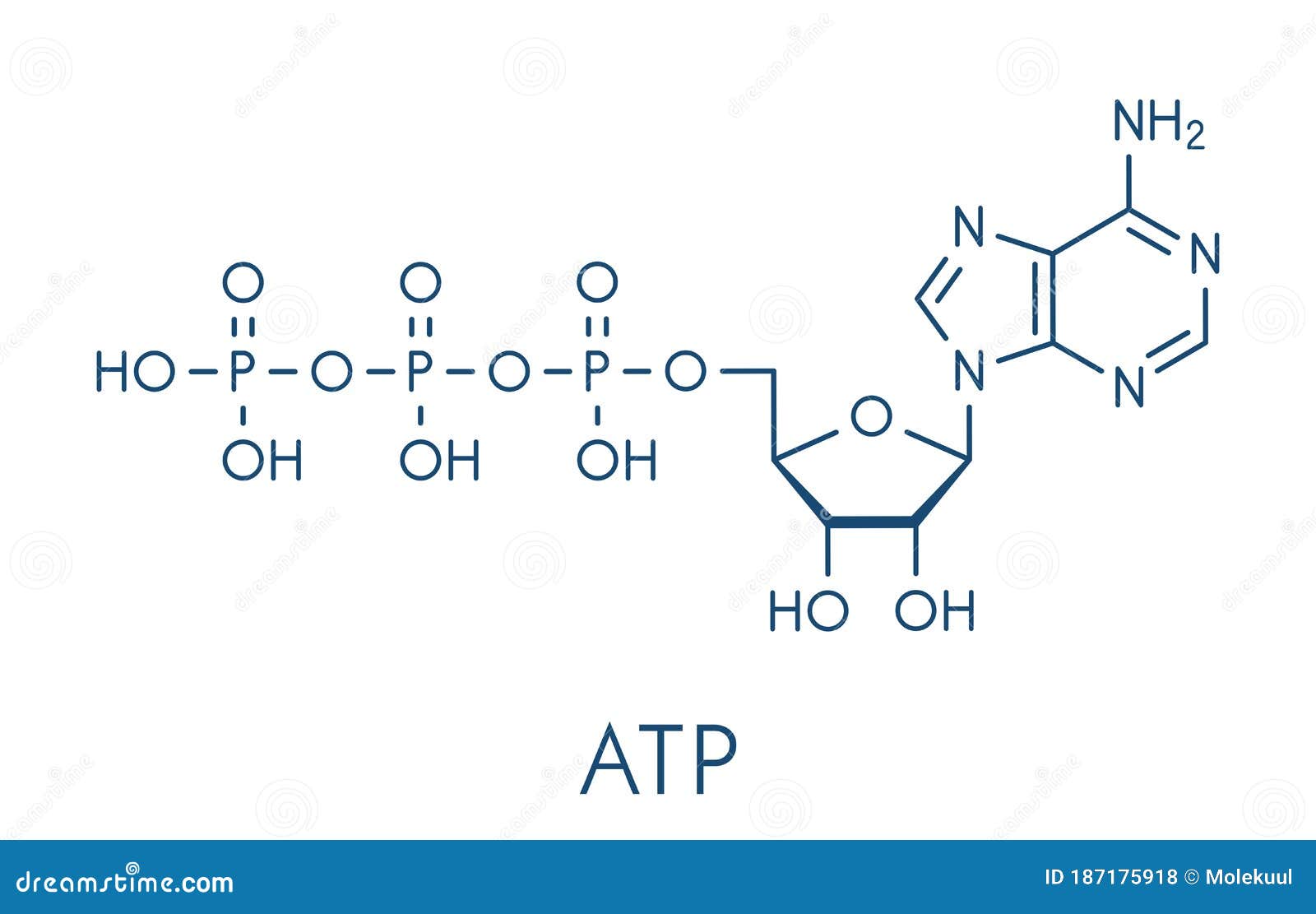
ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate | OpenStax Biology 2e - Lumen Learning ATP is the primary energy-supplying molecule for living cells. ATP is comprised of a nucleotide, a five-carbon sugar, and three phosphate groups. The bonds that connect the phosphates (phosphoanhydride bonds) have high-energy content. The energy released from ATP hydrolysis into ADP + P i performs cellular work.
Atp molecule with labels
RCSB PDB - ATP Ligand Summary Page nutraceutical. Description. An adenine nucleotide containing three phosphate groups esterified to the sugar moiety. In addition to its crucial roles in metabolism adenosine triphosphate is a neurotransmitter. Synonyms. Adenosine-5'-triphosphate. Adenosine triphosphate disodium trihydrate. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - HHMI BioInteractive Description This model shows the structure of ATP, a molecule that provides energy for cellular processes, including protein phosphorylation. ATP has many important roles in the cell. A major role of ATP is to bind to and activate enzymes called kinases. › articles › s41467/022/31945-6Cross-validation of distance measurements in proteins by ... Jul 29, 2022 · Pulsed electron-electron double resonance spectroscopy (PELDOR/DEER) and single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer spectroscopy (smFRET) are frequently used to determine conformational ...
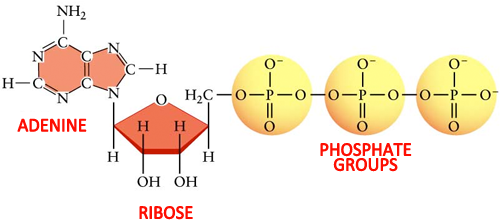
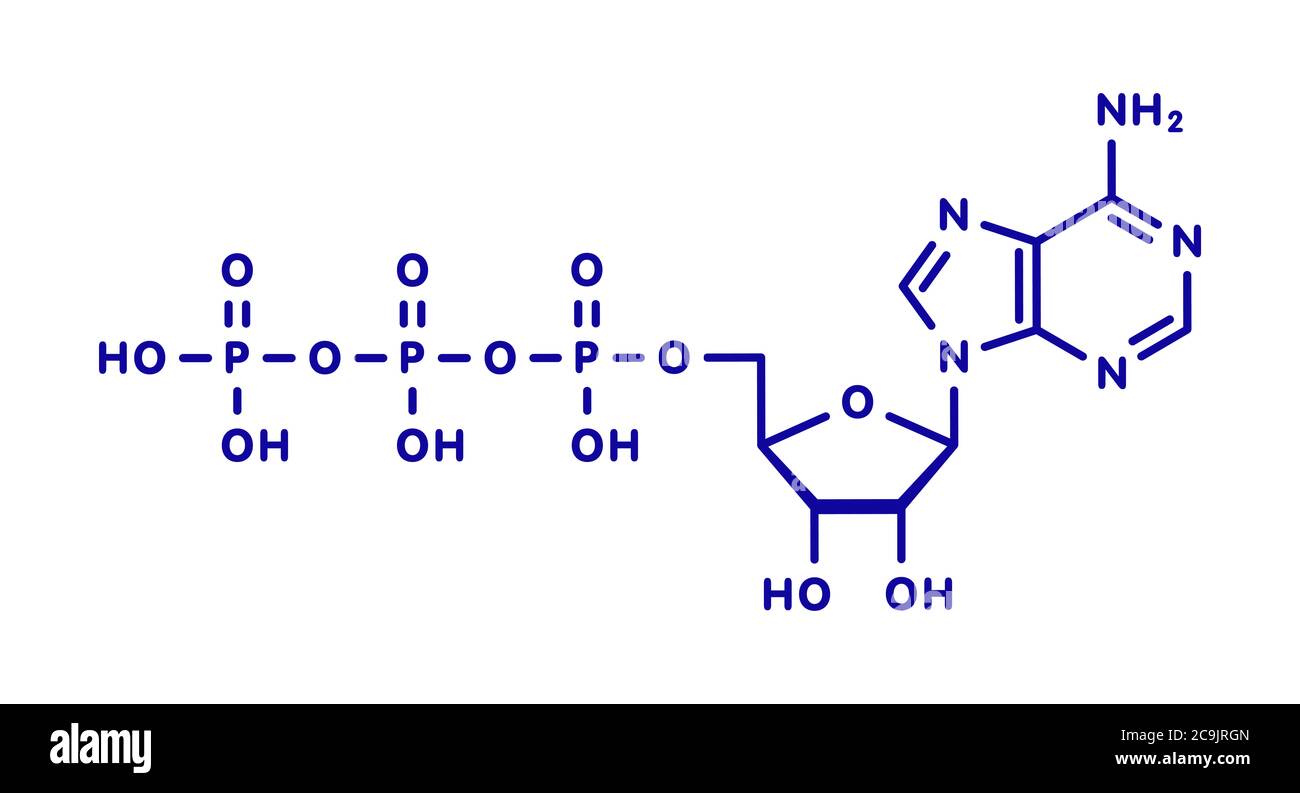
Atp molecule with labels. CRISPR/Cas-engineered technology: Innovative approach for … In the absence of ATP, the specific aptamer, as the DNA activator, was engaged in the interaction with the Cas12a/CrRNA conjugate, inducing the trans-cleavage of the DNA reporter labeled with the fluorophore-quencher pair through the activation of Cas12a enzyme. So, a significant fluorescence output signal was obtained by getting the labels away from each other. In the … Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP. What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine. Ribose. Three Phosphate Groups. Here is a picture: › books › NBK26894The Mitochondrion - Molecular Biology of the Cell - NCBI ... In the mitochondria, the metabolism of sugars is completed, and the energy released is harnessed so efficiently that about 30 molecules of ATP are produced for each molecule of glucose oxidized. By contrast, only 2 molecules of ATP are produced per glucose molecule by glycolysis alone. Mitochondria can use both pyruvate and fatty acids as fuel.
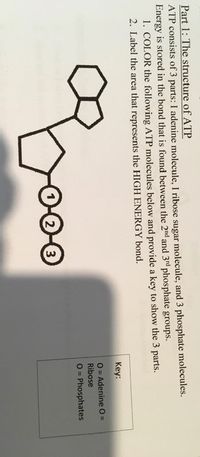
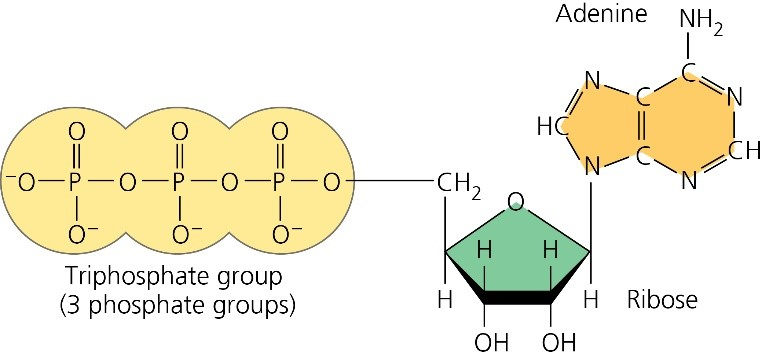
The ATP Molecule -Chemical and Physical Properties - World of Molecules The Adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. For 3-D Structure of this image using Jsmol Click here atp molecule Flashcards and Study Sets | Quizlet Biological molecules, Enzyme, DNA, ATP. Polymerase. Monomers. Describe how glucose join form maltose. A large complex molecules composed by a long chain of monomers…. Are small repeat basic molecular unit, which form large molecu…. 1. two glucose combine remove water molecule,... 2. From between…. quizlet.com › 548952862 › unit-6-flash-cardsUnit 6 Flashcards | Quizlet View the illustration, and drag the labels to their appropriate place. 3 Label the anterior view of the lower respiratory tract. Label the anterior view of the lower respiratory tract based on the hints if provided. Describe the three parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers The parts of a molecule of ATP are:* the purine base, adenine, linked to * the sugar, ribose, linked to * a chain of three phosphate groups. ... Label the parts of an ATP molecule? Adedine, Ribose ...
Mastering Biology 5 Flashcards | Quizlet Drag the labels onto the table to indicate when each statement is true. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. 1. Orange dye moves independently of purple dye 2. Concentration gradients exist that drive diffusion of both dyes 3. There is a net movement of orange dye from side A to side B 4. Purple dye moves only from side B to side A 5. There is no net movement of … How Does ADP Become ATP? Cycle, Structure, and Function - Study.com ATP is made up of adenine, ribose, and three phosphate molecules. ATP contains one adenine (blue), one sugar (pink), and three phosphate groups. ATP Meaning ATP follows the same rules of... 1Q1K: Structure Of Atp-phosphoribosyltransferase From E. Coli Complexed ... ATP PHOSPHORIBOSYLTRANSFERASEL(+)-Tartaric AcidPhosphoribosyl Atp. NCBI. National Center for Biotechnology Information. ... Label Count Molecule; Proteins (6 molecules) A. A_1. A_2. A_3. A_4. A_5. 6: ATP Phosphoribosyltransferase (Gene symbol: hisG) Chemicals and Non-standard biopolymers (18 molecules) 1. 6. ATP Diagram | Quizlet a lower-energy molecule that can be converted into ATP. Tri. three. Di. two. ATP Cycle. a cycle that converts ADP into ATP & ATP releases energy and turns into ADP. Phosphate Group (removed) a phosphate is removed to release energy. Phosphate Group (added) A phosphate group is added using a small amount of energy.
Label Atp Molecule - the atp molecule chemical and physical properties ... Label Atp Molecule - 16 images - 35 label each part of the atp molecule labels database 2020, photosynthesis light reactions, energy atp and adp sciencemusicvideos, simple diagram atp molecule diagramaica,
Chapter 1: Acid–Base Reactions – OCLUE: Organic Chemistry, Life, … In the case of reactions that occur within aqueous solution, the H + is transferred to a water molecule to form H 3 O +. Consider, as an example, HCl; in aqueous solution HCl transfer a H + group to a water molecule. The products are H 3 O + (the conjugate acid of water) and Cl –, the conjugate base of HCl.
Nucleotide - Wikipedia A nucleotide is composed of three distinctive chemical sub-units: a five-carbon sugar molecule, a nucleobase—the two of which together are called a nucleoside—and one phosphate group.With all three joined, a nucleotide is also termed a "nucleoside monophosphate", "nucleoside diphosphate" or "nucleoside triphosphate", depending on how many phosphates make up the …
atp molecule labeled - davincifireplace Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below. In the yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe the FANCM-family DNA helicase FmI1 directs NCO recombination formation during meiosis. u Based on these helicase motifs, a number of helicase superfamilies have been distinguished. In: Spies, M.
Label the parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and...
rysesupps.com › products › creatine-monohydrateCreatine Monohydrate | RYSE Supplements Creatine is stored in the muscle as creatine phosphate. Those familiar know ATP, cellular energy, is adenosine triphosphate. There’s something special about those phosphates. When they are clipped off the parent molecule, they release a ton of energy. The cell is able to harvest this energy and put it to work.
Cross-validation of distance measurements in proteins by ... - Nature 29.07.2022 · Pulsed electron-electron double resonance spectroscopy (PELDOR/DEER) and single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer spectroscopy (smFRET) are frequently used to determine conformational ...
Which label identifies the part of the ATP molecule that changes when ... Answer: C; respiration. Explanation: Cellular respiration is the process by which nutrients such as glucose are broken down using oxygen to generate energy in the form of ATP, that is used to drive cellular processes.; ATP consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phosphate groups in a row. Energy from cellular respiration is stored in the bond between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups ...
Creatine Monohydrate | RYSE Supplements Creatine is stored in the muscle as creatine phosphate. Those familiar know ATP, cellular energy, is adenosine triphosphate. There’s something special about those phosphates. When they are clipped off the parent molecule, they release a ton of energy. The cell is able to harvest this energy and put it to work. In the muscle, this powers ...
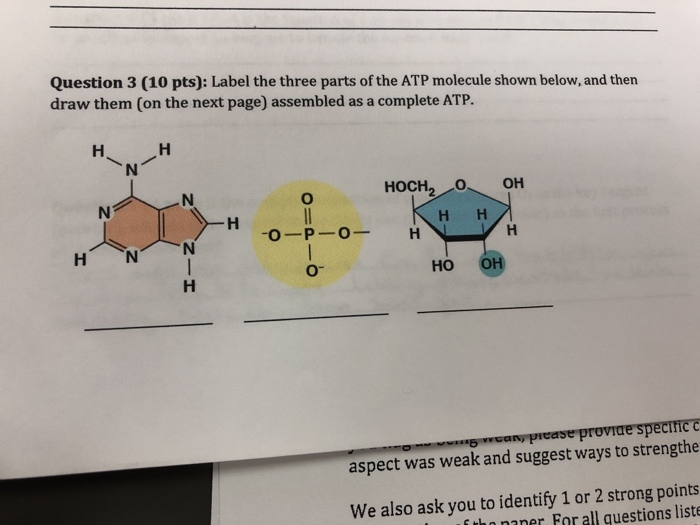
Solved Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule - Chegg 100% (1 rating) 7. From left to right- Adenine - Ribose - Phosphate groups 8. The low battery represents an ADP molecule. Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP results in loss of phosphate group. hence ADP + Pi is low energy state during ATP (energy carrier) … View the full answer Transcribed image text: Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below.
PDF worksheet chemical energy and ATP - SC TRITON Science Identify the parts of an ATP molecule below: (Label adenosine, ribose, ... What happens to the ATP molecule when a phosphate group is removed ? (what does it turn into?) 8. Draw a diagram below showing the cycle of ATP and ADP below (see Figure 4.2 on page 101) 9. What type of organic compounds store the most energy?
The Mitochondrion - Molecular Biology of the Cell - NCBI … The cell was stained with a fluorescent dye (rhodamine 123) that specifically labels mitochondria Figure 14-6 ... Although the exact number of protons needed to make each ATP molecule is not known with certainty, we shall assume that one molecule of ATP is made by the ATP synthase for every 3 protons driven through it. Whether the ATP synthase works in its ATP-synthesizing …
ATP Molecule Structure: Fuel of Life - Indigo Instruments ATP is composed of the nitrogenous base adenine, the five-carbon sugar ribose, and three phosphate groups. Energy is released when it loses a phosphate group as it goes from ATP it becomes ADP or Adenosine Diphosphate.
1 draw and label an atp molecule make sure to include 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Make sure to include the 3 parts. 2. What is the process called when a phosphate is added to the ADP molecule a. Photosynthesis b. Phosphorylation c. Permeability d. Precipitation 3. The metabolism (breakdown) of ________________ in the mitochondria provides the energy for the phosphorylation ofADP.a. ATP b.
2ATP: Crystal Structure Of A Cd8ab Heterodimer Label Count Molecule; Proteins (3 molecules) A. 1: T-cell Surface Glycoprotein CD8 Alpha Chain. E. 1: Artifact Linker. B. 1: T-cell Surface Glycoprotein CD8 Beta Chain. Chemical and Non-standard biopolymers (1 molecule) 1: 1. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine * Click molecule labels to explore molecular sequence information.
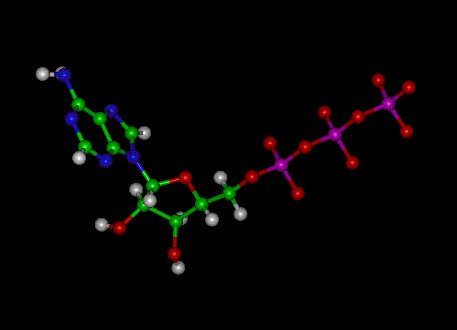
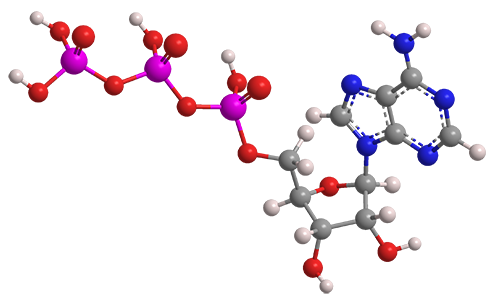
The ATP molecule in 3-D - BioTopics The ATP molecule - rotatable in 3 dimensions The ATP (adenosine triphosphate) molecule has 3 main parts: the base adenine - a double ring like section with several nitrogen atoms (blue), the 5 carbon sugar ribose in the centre, and 3 phosphate groups - a row of phosphorus atoms (orange) surrounded by oxygens (red).
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › NucleotideNucleotide - Wikipedia A nucleotide is composed of three distinctive chemical sub-units: a five-carbon sugar molecule, a nucleobase—the two of which together are called a nucleoside—and one phosphate group. With all three joined, a nucleotide is also termed a "nucleo side mono phosphate", "nucleoside di phosphate" or "nucleoside tri phosphate", depending on how ...
ATP reading and coloring activity.pdf - Read, Answer, Color, Label ... Color and label the matrix (10) yellow on Figure 3. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy molecule used by cells to do work. It is a nucleotide consisting of a nitrogen-containing base (adenine, thymine, cytosine or guanine), a 5-carbon sugar, and 3 phosphate groups. ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells.
ATP and ADP: Definition, Formation, Examples I ResearchTweet There are 3 phosphate molecule and one adenine molecule which forms the ATP. ATP to ADP Energy Release As the ATP molecule consist of 3phosphate molecule and an adenine molecule, thus when ATP is converted to ADP, a phosphate molecule is lost in this process. The reaction can be written as ATP → ADP + P i
BIOL 1020 CH. 7 HW Flashcards | Quizlet Drag the labels onto the table to indicate when each statement is true. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. Some solutes are able to pass directly through the lipid bilayer of a plasma membrane, whereas other solutes require a transport protein or other mechanism to cross between the inside and the …
Adenosine triphosphate - Wikipedia Adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) is an organic compound and hydrotrope that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis.
Solved 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing - Chegg 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy. 2. How is ADP different from ATP? ADD has 2 phosphate ATP has 3 phosphate 3. Explain why glucose is important. groups groups 4. What is glucose broken down into during glycolysis? 5. Where does glycolysis occur? = 6.
quizlet.com › 151764685 › mastering-biology-5-flashMastering Biology 5 Flashcards | Quizlet Drag the labels onto the table to indicate when each statement is true. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. 1. Orange dye moves independently of purple dye 2. Concentration gradients exist that drive diffusion of both dyes 3. There is a net movement of orange dye from side A to side B 4. Purple dye moves only from side B to ...
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate | C10H16N5O13P3 - PubChem Adenosine-5'-triphosphate | C10H16N5O13P3 | CID 5957 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological ...
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Magnesium_in_biologyMagnesium in biology - Wikipedia For example, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the main source of energy in cells, must bind to a magnesium ion in order to be biologically active. What is called ATP is often actually Mg-ATP. As such, magnesium plays a role in the stability of all polyphosphate compounds in the cells, including those associated with the synthesis of DNA and RNA.
DOC Read, Answer, Color, Label: Mitochondria - nsbhigh.com Color and label the matrix (10) yellow on Figure 3. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy molecule used by cells to do work. It is a nucleotide consisting of a nitrogen-containing base (adenine, thymine, cytosine or guanine), a 5-carbon sugar , and 3 phosphate groups ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells.
Structure of ATP - Learn Insta The discovery of ATP was made by Karl Lohman (1929). ATP is a nucleotide consisting of a base-adenine, a pentose sugar-ribose and three phosphate groups. Out of three phosphate groups the last two are attached by high energy rich bonds (Figure 14.3). On hydrolysis, it releases energy (7.3 K cal or 30.6 KJ/ATP) and it is found in all living ...
Biochemistry 6th Edition Textbook Solutions | bartleby Textbook solutions for Biochemistry 6th Edition Reginald H. Garrett and others in this series. View step-by-step homework solutions for your homework. Ask our subject experts for help answering any of your homework questions!
› articles › s41467/022/31945-6Cross-validation of distance measurements in proteins by ... Jul 29, 2022 · Pulsed electron-electron double resonance spectroscopy (PELDOR/DEER) and single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer spectroscopy (smFRET) are frequently used to determine conformational ...
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - HHMI BioInteractive Description This model shows the structure of ATP, a molecule that provides energy for cellular processes, including protein phosphorylation. ATP has many important roles in the cell. A major role of ATP is to bind to and activate enzymes called kinases.
RCSB PDB - ATP Ligand Summary Page nutraceutical. Description. An adenine nucleotide containing three phosphate groups esterified to the sugar moiety. In addition to its crucial roles in metabolism adenosine triphosphate is a neurotransmitter. Synonyms. Adenosine-5'-triphosphate. Adenosine triphosphate disodium trihydrate. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate.





















Post a Comment for "41 atp molecule with labels"